Female cancer patients of reproductive age may be able to retain their fertility during radiation and chemotherapy through treatments that target the DNA damage response in oocytes (the cells that develop into eggs), an approach that works in animal models.
Jackson Laboratory Assistant Professor Ewelina Bolcun-Filas, Ph.D., and Terri L. Woodard, M.D., assistant professor at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, describe the method in “Prolonging Reproductive Life after Cancer: The Need for Fertoprotective Therapies,” an opinion article in Cell Press Trends in Cancer.
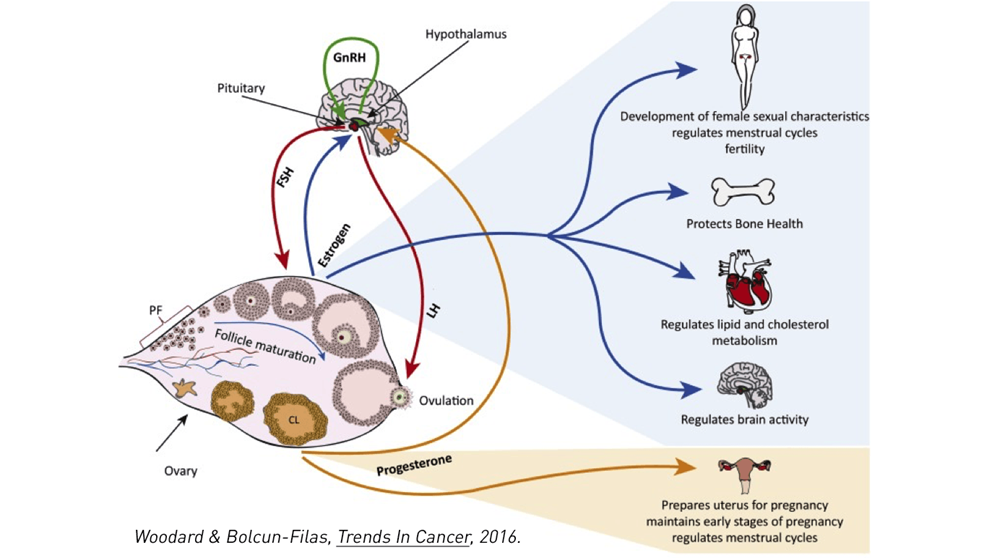
“The good news is that more young women are surviving cancer,” Bolcun-Filas says, “reflecting the advent of better and more efficient therapies. But, many cancer treatments increase the risk of premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) and infertility.” And while assisted reproductive technologies can address infertility, she says, they fail to preserve ovaries’ natural function, which has an important role in women’s health that goes beyond reproduction, including preventing hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Many cancer treatments cause DNA damage, not only in cancer cells, but also normal tissue such as in ovaries. The natural response to this damage is thought to be the elimination of damaged oocytes through apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Recent studies in mice by Bolcun-Filas and other researchers demonstrate that targeting proteins involved in apoptosis protects oocytes and prevents infertility in females exposed to radiation.
For the Trends in Cancer article, the researchers reviewed findings demonstrating how cancer therapies induce apoptotic death in oocytes, and how this knowledge could be applied to design better fertoprotective treatments.
“A better appreciation of oocyte response to radiation and anticancer drugs will uncover new targets for the development of specialized therapies to prevent ovarian failure,” the researchers state.
Woodward and Bolcun-Filas: Prolonging Reproductive Life after Cancer: The Need for Fertoprotective Therapies. Trends in Cancer, May 17, 2016, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2016.03.006.